Main Infrastructures
CAT-ACT (Topic 1)
Spectroscopic Methods & Beamline Operation
X-ray spectroscopy techniques employing highly brilliant synchrotron radiation generated by the electron storage ring KARA at KIT Campus North provide unique insight into atomic or molecular structures of materials which are of pivotal importance in the context of the nuclear waste disposal safety case, e.g., the speciation of radionuclides like actinides or radioactive fission and activation products in highly active nuclear waste (HAW) matrices.

COSMOS (Topic 2)
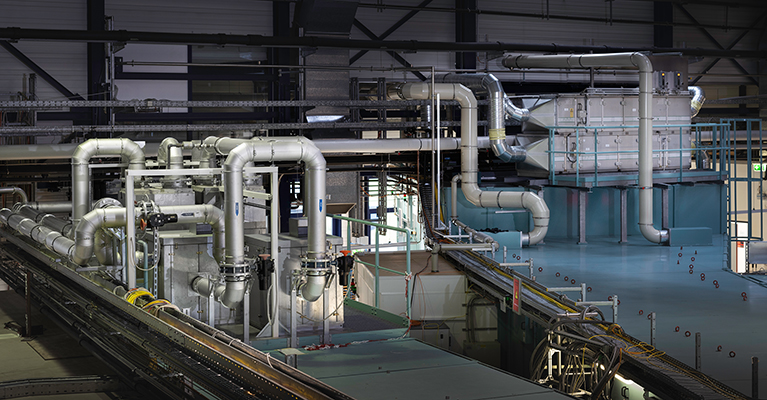
COSMOS-H: Criticalheat flux On Smoothand MOdified Surfaces- Highpressure loop
The experimental facility for thermohydraulics COSMOS-H is used to investigate boiling phenomena and complex flow phenomena which potentially occur in power plants. Research projects are currently focusing on the physics of heat transfer under high-pressure conditions, such as flow boiling, up to the critical heat flux.

COSMOS-L: Critical-heat-flux On Smooth and Modified Surfaces – Low pressure loop
The COSMOS-L thermohydraulics trainer (Figure 1) is used to study complex flow and heat transfer phenomena in boiling flows relevant to power engineering. The facility is operated with fully demineralized water as the experimental medium and is electrically heated. Powerful measurement and control technology allows measurements up to boiling cries.

HOVER (Topic 1)
Helmholtz Research and Technology Platform for the Decommissioning of Nuclear Facilities and for the Management of Radioactive Waste.
The HGF centers FZJ, HZDR and KIT cooperating in the NUSAFE consortium are implementing the laboratory infrastructure HOVER since 2020 as a decentralized research infrastructure. HOVER is dedicated to support advanced scientific investigations and technical developments in the context of the German phase out of nuclear energy.
KALLA - KArlsruhe Liquid Metal Laboratory (Topic 2)
The Karlsruhe Liquid metal Laboratory develops and operates liquid metal loops from laboratory to demonstration scale. Various experiments are carried out on the flow characterisation and heat transfer of so-called liquid metals flowing through generic or complex geometries.

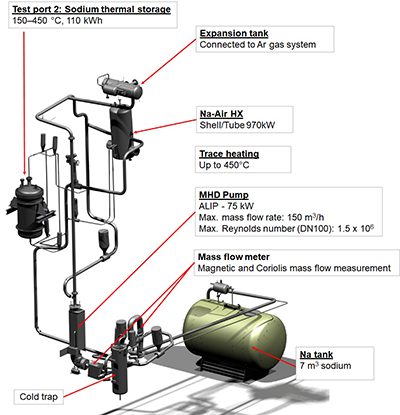
KASOLA - KArlsruhe SOdium Laboratory (Topic 2)
The KArlsruhe SOdium LAboratory at KIT is a versatile experimental facility to investigate flow phenomena in liquid sodium. A key feature of the KASOLA facility is its flexibility, enabling the conduction of a wide spectrum of thermal-hydraulic experiments for solar and nuclear applications (fission and fusion).
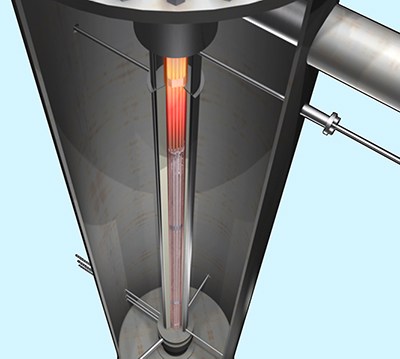
QUENCH (Topic 2)
An important accident management measure for controlling severe accident transients in light water reactors (LWRs) is the injection of water to cool the degrading core. Flooding of the overheated core, which causes quenching of the fuel rods, is considered a worst-case scenario regarding hydrogen generation rates which should not exceed safety-relevant critical values. Therefore, a research program on reflood of an overheated core and corresponding topics is running at KIT, including large scale bundle tests, various kinds of separate-effects tests, model development and code application.